This comprehensive guide will give you everything to know about TRT, from diagnosis, treatment, and potential risks to long-term benefits for body, mind, and libido.
In 2021, 2.3 million American men were prescribed testosterone replacement therapy (TRT)—nearly triple that of 2011. The benefits of TRT include increased energy, muscle mass, and libido, but there is intense debate about this medical wonder drug.
Testosterone is fundamental to male vitality and impacts nearly every aspect of a man’s health—from physical strength and energy levels to mood and sexual function. However, as men age or develop certain health conditions, testosterone levels naturally decline. This drop can lead to a number of problematic symptoms, such as chronic fatigue, diminished libido, weight gain, and cognitive difficulties.
But the good news is that treatment options are available. Testosterone Replacement Therapy or “TRT” is an effective medical solution for men struggling with low testosterone.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the science behind testosterone therapy and its medical benefits, risks, and best practices for those considering or undergoing treatment.
1. Introduction to Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
What is Testosterone?
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone, and it’s essential for the development and maintenance of male physical traits. But its functions extend well beyond that. It plays a vital role in men’s overall health and influences muscle mass, bone density, fat distribution, red blood cell production, and even mental health. As a result, testosterone impacts energy levels, mood, sexual function, and cognitive performance.
The testicles produce testosterone, and the hypothalamus and pituitary gland in the brain regulate production, which forms a hormone feedback loop in men’s physiology.
Testosterone plays a vital role in male puberty—it deepens the voice, encourages facial hair growth, and drives muscle development—but it remains important for vitality and well-being throughout a man’s life.
Why Testosterone Levels Decline
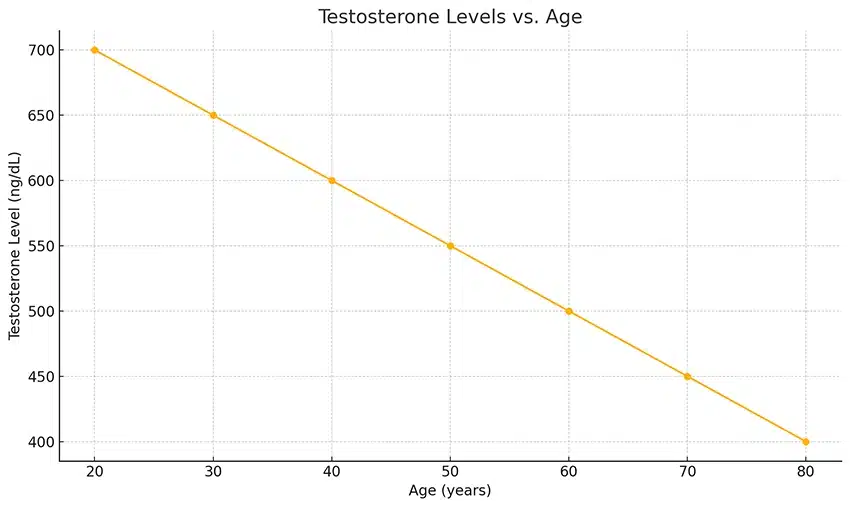
Testosterone production naturally declines with age. Men typically reach their peak testosterone levels in their late teens and early 20s. After the age of 30, testosterone levels begin to decrease gradually at an average rate of about 1% per year. This decline is normally due to the natural aging process, but several factors can exacerbate it, including:
- Chronic stress: High levels of the stress hormone cortisol can inhibit testosterone production.
- Lack of physical activity: Exercise—especially weight training—stimulates hormone production, but a sedentary lifestyle reduces testosterone.
- Obesity: Higher body fat levels disrupt hormonal balance and lead to lower testosterone.
- Poor sleep: Sleep deprivation, particularly the lack of deep sleep, impairs testosterone production.
- Medical conditions: Diabetes, sleep apnea, and other chronic conditions are associated with lower testosterone levels.
Many men experience noticeable symptoms due to this natural decline, including fatigue, reduced libido, difficulty concentrating, and muscle loss. For some men, these changes are subtle, but for others, the impact on quality of life is profound. When testosterone levels drop significantly, it may lead to a condition known as hypogonadism, and medical intervention through Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) can be beneficial.
Overview of Testosterone Replacement Therapy
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a treatment designed to restore testosterone levels in men with clinically low levels. It addresses testosterone deficiency, which often increases among men as they age.
TRT supplements the body’s natural testosterone production to alleviate symptoms associated with low testosterone and improve overall well-being.
There are several TRT treatment options:
- Injections: Testosterone is injected into the muscle, typically once every 1-2 weeks, for a long-lasting boost of testosterone levels.
- Topical gels and creams: These are applied daily to the skin, allowing testosterone to be absorbed into the bloodstream gradually.
- Patches: Similar to gels, testosterone patches are applied to the skin and release testosterone steadily throughout the day.
- Pellets: Small pellets implanted under the skin release testosterone slowly over the course of several months.
The goal of testosterone therapy is to raise testosterone levels to a healthy range that alleviates symptoms and supports optimal functioning. For many men, testosterone treatment offers significant improvements in energy, mood, and physical health, but a medical professional must prescribe and monitor treatment to ensure proper dosing and mitigate potential side effects.
2. The Role of Testosterone in Men’s Health
Testosterone impacts nearly every aspect of a man’s health. Beyond its role in physical development, it plays a central role in maintaining the body’s systems and functions. Here’s how testosterone influences physical, mental, and sexual health in men.
Testosterone and Physical Health
- Muscle mass and bone density: Since testosterone increases the production of proteins that build muscle fibers, it maintains muscles, promotes strength, and contributes to overall physical performance. It also increases bone density to prevent osteoporosis and reduce the risk of fractures as men age.
- Heart health and circulation: Healthy testosterone levels support cardiovascular health through red blood cell production, which is essential for oxygen transport throughout the body. There is an established link between low testosterone levels and an increased risk of heart disease, though researchers are still studying the exact relationship between testosterone and heart health.
- Cognitive function and memory: Research shows that testosterone supports brain function, particularly memory and concentration. Some studies suggest that low testosterone levels may contribute to cognitive decline in aging men, so it’s a key hormone for mental sharpness and clarity.
Testosterone and Mental Health
- Mood regulation and depression: Testosterone influences brain chemistry and the neurotransmitters that regulate mood. Low testosterone levels can cause symptoms of depression, irritability, and low motivation. Men undergoing TRT frequently report improved mood stability and reduced feelings of sadness or frustration.
- Dopamine production and motivation: Testosterone boosts dopamine production, a neurotransmitter that plays a significant role in motivation, reward, and pleasure. Healthy testosterone levels contribute to a greater sense of drive and accomplishment.
Testosterone and Sexual Health
- Libido and sexual performance: Testosterone directly affects men’s libido (sex drive) and sexual function. Low testosterone can reduce sexual desire, cause difficulty achieving or maintaining erections, and lead to overall dissatisfaction with sexual performance. Men who restore their testosterone levels through TRT often rejuvenate their sexual health and increase desire and satisfaction.
Testosterone forms the foundation for overall well-being and influences everything from physical strength to emotional balance. Since the hormone plays such a critical role in men’s health, TRT can be a life-changing treatment for those with testosterone deficiency.
3. Benefits of Testosterone Therapy
TRT offers significant improvements for men who suffer from low testosterone levels. The treatment goal is to restore testosterone to healthy levels, which can lead to a variety of physical and mental benefits. The most well-documented advantages of testosterone therapy include:
Improved Physical Strength and Muscle Growth
One of the most immediate and noticeable benefits of testosterone therapy is an increase in muscle mass and physical strength. Testosterone plays a critical role in protein synthesis, the process by which the body builds and repairs muscle tissue.
Men on TRT often experience enhanced muscle growth and find it easier to gain strength and recover from workouts. This is particularly important for aging men, as muscle mass naturally declines with age, which leads to frailty and a higher risk of injury.
Studies show that men undergoing TRT see improvements in both muscle size and power, so it’s an effective option for those who want to maintain or regain their physical prowess as they age.
Fat Loss and Body Composition Improvements
In addition to muscle growth and support, testosterone regulates fat metabolism. Men with low testosterone levels often struggle with weight gain, particularly around the abdomen. TRT increases the body’s metabolic rate and improves insulin sensitivity for more efficient fat burning and body fat reduction.
As a result, many men on TRT notice significant changes in their body composition, including increased lean muscle mass and decreased fat, especially in stubborn areas like the belly.
Enhanced Libido and Sexual Function
Testosterone is a key hormone for sexual health. Men with low testosterone frequently experience a decrease in libido (sex drive) and sexual performance issues, such as difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection. TRT can restore sexual desire and improve erectile function for enhanced sexual performance and satisfaction.
Since numerous studies confirm the link between testosterone levels and sexual health, TRT is a common treatment for men with sexual dysfunction related to low testosterone.
Better Mood and Mental Clarity
Testosterone contributes to mental and emotional well-being as well. Low testosterone levels can lead to symptoms of depression, irritability, and a general lack of motivation. Many men feel more mentally sharp, emotionally balanced, and motivated after starting testosterone therapy.
In addition to mood improvements, TRT can also enhance cognitive function. Testosterone affects memory and focus, which is particularly important for older men concerned about cognitive decline. TRT restores hormone levels for better mental clarity and sharpness.
Prevention of Osteoporosis and Frailty in Aging Men
As men age and their testosterone levels drop, they become more susceptible to osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones and increases the risk of fractures.
TRT maintains and even improves bone density, which is especially important for older men who want to stay active and avoid injury.Stronger bones and increased muscle mass make it easier for men to stay physically independent as they age.
4. Potential Risks and Side Effects of TRT
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) offers numerous benefits, but it’s important to be aware of the potential risks and side effects associated with the treatment. Like any medical intervention, men should only receive TRT from a licensed healthcare provider to minimize complications. Here are some of the most common risks and side effects to consider:
Hormonal Imbalance (Estrogen and DHT)
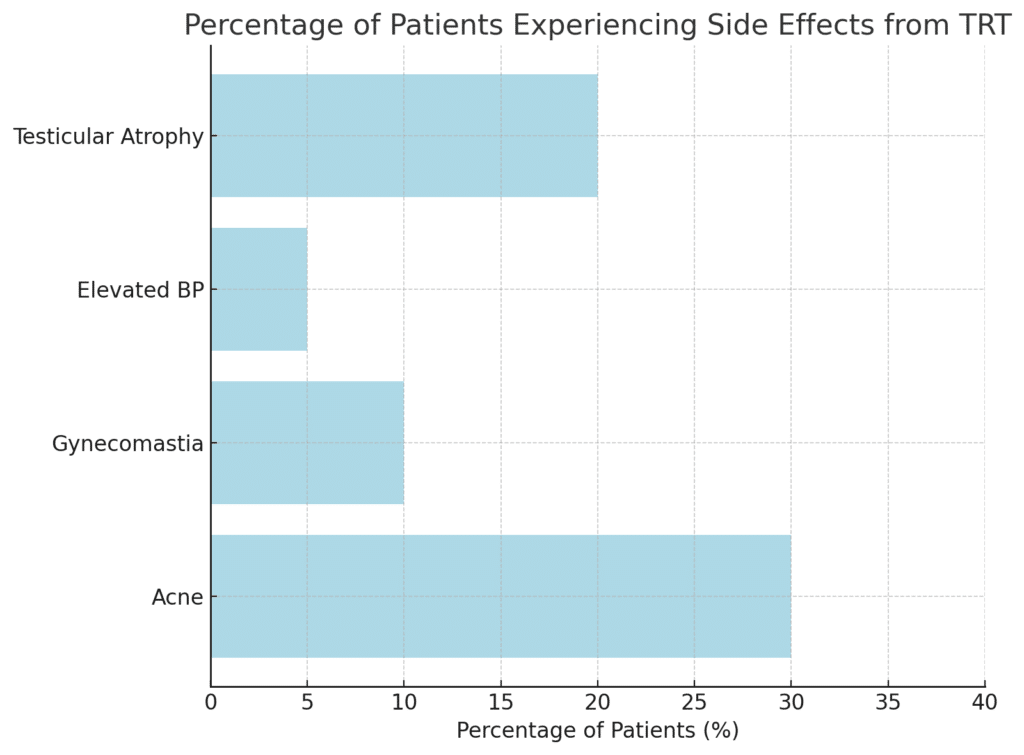
Testosterone doesn’t act in isolation—it can convert into other hormones, such as estrogen and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Elevated estrogen levels in men can lead to unwanted side effects like water retention and gynecomastia (enlarged breast tissue), while high levels of DHT may cause hair loss and acne.
Doctors who offer TRT regularly monitor hormone levels to ensure a balanced treatment and minimal side effects. They may prescribe medications to prevent or manage any hormonal imbalances, such as aromatase inhibitors to control estrogen or DHT blockers to prevent hair loss.
Gynecomastia (Enlarged Breast Tissue)
Gynecomastia is a potential side effect of testosterone therapy, especially if testosterone converts into estrogen at a high rate. This condition causes men’s breast tissue to enlarge, which can be uncomfortable or cause emotional distress. While not dangerous, it is a cosmetic concern for many men. In some cases, a doctor may adjust the TRT dosage or use estrogen-blocking medications to prevent this issue.
Cardiovascular Risks and Monitoring
The relationship between TRT and cardiovascular health is a subject of debate. Medical professionals once believed that there was a link between testosterone therapy and an increased risk of heart attacks, strokes, or other cardiovascular issues, including high blood pressure, especially in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions.
However, more recent clinical research studies show no significant increase in cardiovascular risks for men on testosterone therapy.
But it’s important to discuss your cardiovascular health with your doctor before you start TRT, especially if you have a history of heart disease. Your doctor should regularly monitor your blood pressure and cholesterol levels to mitigate potential cardiovascular risks.
Impact on Prostate Health
Since there is a link between testosterone and prostate health, there are concerns that testosterone therapy could increase the risk of prostate cancer or exacerbate pre-existing conditions.
While men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) may experience worsening symptoms if they undergo TRT, recent studies show no strong evidence linking TRT to an increased risk of prostate cancer in men without a prior diagnosis.
That said, testosterone can stimulate the growth of existing prostate cancer, so men with a history of the disease should exercise caution and undergo regular prostate exams during TRT.
Acne, Hair Loss, and Other Skin Conditions
As testosterone levels increase, some men experience side effects like acne, oily skin, or hair loss. Some may also experience increased body hair growth on areas like the back and chest. This is particularly common in men who are genetically predisposed to these conditions. Elevated DHT, a byproduct of testosterone, can lead to male pattern baldness and skin issues like acne.
These side effects are generally mild and manageable, but they are frustrating for some men. Dermatological treatments or TRT dosage adjustments help mitigate these skin-related side effects.
When men understand the benefits and potential risks of Testosterone Replacement Therapy, they can make informed decisions about their treatment options. TRT can significantly improve quality of life, but it’s important to work with a healthcare provider to monitor hormone levels and minimize side effects.
5. Who Should Consider TRT?
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is not for everyone. It’s specifically designed for men who suffer from low testosterone (hypogonadism) and experience related symptoms that affect their quality of life. So before you consider TRT, you need to know the symptoms of low testosterone and get an official diagnosis.
Symptoms of Low Testosterone
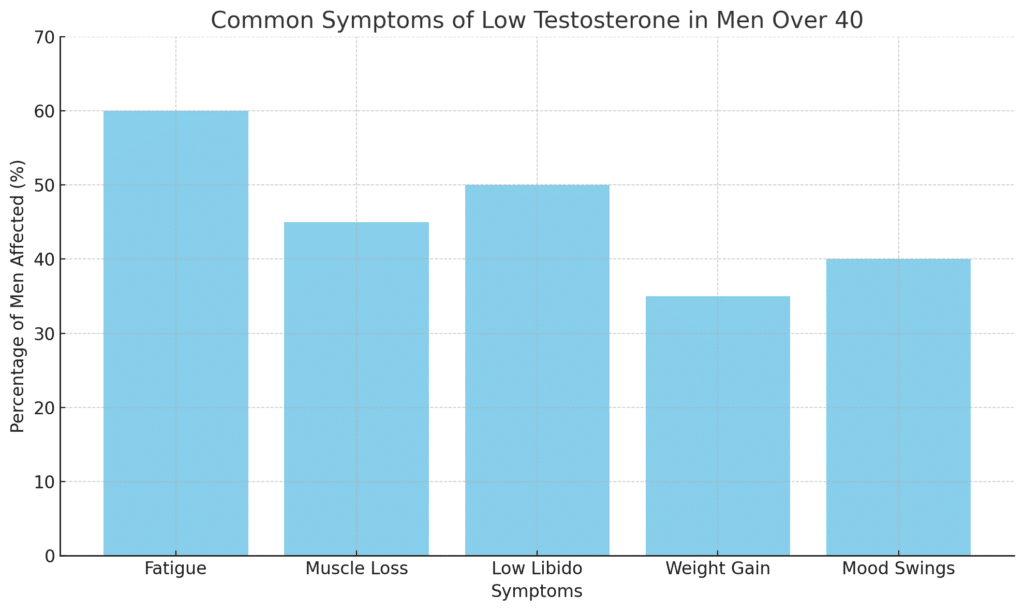
Testosterone plays a vital role in various bodily functions, so when levels drop below normal, a range of symptoms can occur. Men with low testosterone may notice the following signs:
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness or low energy levels, even after a full night’s sleep, is a common symptom of low testosterone. Men often feel a lack of motivation or general sluggishness.
- Depression and irritability: Testosterone influences mood regulation. Low levels can lead to feelings of depression, irritability, and anxiety. Many men report a sense of emotional imbalance when their testosterone dips.
- Weight gain: Men with low testosterone may experience weight gain and an increase in body fat. It can be particularly difficult to shed fat around the midsection, and muscle loss can compound this issue.
- Sexual dysfunction: Testosterone affects libido and sexual function. Men with low testosterone often experience a decrease in sexual desire and may struggle with erectile dysfunction or other issues related to sexual performance.
Nearly everyone experiences these issues at some point in their lives, and if these symptoms persist, it may indicate a more serious testosterone deficiency that could benefit from TRT.
Diagnosing Low Testosterone
Before you start TRT, you need a proper diagnosis from a healthcare provider, which involves both clinical evaluation and laboratory testing.
Blood Tests and Medical Evaluation
A blood test is the most reliable way to measure testosterone levels. Doctors typically measure testosterone in the morning when levels are at their highest.
A normal range for testosterone is between 300 and 1,000 ng/dL. Men with levels below 300 ng/dL, along with symptoms of deficiency, may be candidates for TRT. However, a single blood test may not be enough, and your doctor may recommend multiple tests to confirm a low testosterone diagnosis.
🔗 Should you get a testosterone test? Check out our full guide on testosterone testing and how to get a free test.
Androgen Deficiency and Hypogonadism
Several factors can cause low testosterone. Primary hypogonadism occurs when the testicles fail to produce adequate testosterone, while secondary hypogonadism involves problems with the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, which regulate hormone production.
Androgen deficiency can result from genetics, injury, illness, or simply the aging process. Your doctor will test for the root cause of low testosterone to determine the most appropriate treatment.
Testosterone Treatment for Age-Related Decline vs. Medical Conditions
Doctors prescribe TRT for two main reasons:
- Age-related testosterone decline: As men age, testosterone naturally decreases. This is known as “andropause” or age-related testosterone decline. Many men turn to TRT to counter the physical and emotional effects of this natural decline, such as fatigue, decreased libido, and muscle loss.
- Medical conditions: Some men experience low testosterone due to medical conditions like hypogonadism, diabetes, or autoimmune disorders. In these cases, TRT can be necessary to manage symptoms and maintain quality of life.
For men who suffer from either age-related decline or a diagnosed medical condition, TRT offers a viable solution to restore low-T levels and improve overall well-being.
6. TRT Treatment Options
After a low testosterone diagnosis, the next step is deciding on the most appropriate method of testosterone delivery. There are several TRT options available, each with its own benefits and considerations. Here are the most common TRT methods:
Injectable Testosterone
Injectable testosterone is one of the most common and effective forms of TRT. With this method, medical personnel can administer testosterone in the clinic, or the patient can self-administer it at home, delivering testosterone directly into the muscle, typically in the gluteal or thigh area, every 1–2 weeks, depending on the formulation.
Testosterone Cypionate, Enanthate, and Propionate
There are three primary types of injectable testosterone:
- Testosterone cypionate: This is the most widely used form of injectable testosterone. It has a longer half-life and requires injections every 1–2 weeks.
- Testosterone enanthate: This is another long-acting testosterone injection with a 1–2 week treatment schedule.
- Testosterone propionate: Unlike the other two, propionate is shorter-acting and requires more frequent injections, typically every 2–3 days. It’s less commonly used due to the inconvenience of frequent administration.
Injectable testosterone is effective and relatively low cost, but it requires routine injections, which some men find inconvenient.
Topical Gels, Creams, and Patches
For men who prefer to avoid needles, topical gels, creams, and patches are popular alternatives. These products go directly on the skin and are absorbed into the bloodstream.
- Gels and creams: These require daily application to areas like the shoulders, arms, or abdomen. Gels are fast-absorbing and effective, but you have to take care to avoid transferring testosterone to others through skin contact.
- Patches: Testosterone patches stay on the skin and deliver a steady release of testosterone over 24 hours. They are convenient but may cause skin irritation in some men.
Topical solutions are less invasive, but you have to apply them consistent every day to maintain stable testosterone levels.
Nasal Gels and Buccal Preparations
Nasal gels and buccal (oral) preparations are newer forms of TRT designed for men who want an alternative to injections and topical treatments.
- Nasal gels: These gels are applied inside the nostrils multiple times a day. While effective, they require frequent application, which may be inconvenient for some.
- Buccal tablets: As these small tablets dissolve inside the mouth, between the gum and cheek, the bloodstream absorbs the testosterone through the mucous membrane. This method is the least common, but it is another option for men who prefer oral administration.
Testosterone Pellets
Testosterone pellets are a long-acting form of TRT. A doctor implants these small pellets under the skin, typically in the buttocks or hip area. The pellets slowly release testosterone over 3–6 months—no need for frequent injections or daily applications. While convenient, pellet implantation is a minor surgical procedure that requires periodic replacement.
Oral Testosterone
Oral testosterone is the least commonly prescribed form of TRT due to concerns about liver health. Unlike other forms of testosterone delivery, oral testosterone must pass through the liver, which can lead to liver damage or other complications. Most doctors prefer other methods of administration that bypass the liver.
There’s no “right” TRT treatment option—it depends on personal preferences, lifestyle, and medical needs. Each method has its advantages and drawbacks, and a healthcare provider will help you determine which option best suits your goals and health conditions.
7. The Optimal TRT Protocol
Testosterone treatment is not a one-size-fits-all process. Each man’s body responds differently to testosterone, so it’s essential to customize the therapy for optimal results. A well-planned TRT protocol requires the right dosage, a sustainable frequency of administration, and regular progress monitoring.
How to Choose the Right TRT Protocol
Doctors design unique TRT protocols for each patient based on individual testosterone levels, the severity of symptoms, lifestyle preferences, and any underlying medical conditions. Here’s what to consider:
Dosage, Frequency, and Monitoring
The appropriate milligrams (mg) dosage of testosterone varies from person to person. Your doctor will prescribe an initial dose based on your testosterone levels and symptoms. They will likely start conservatively to avoid side effects, but over time, they may raise the dosage based on your body’s response to the treatment.
- Injectable testosterone: You’ll get an injection every 1-2 weeks, depending on the type of testosterone your doctor prescribes. They may allow you to self-administer at home or require you to come into their office for treatment.
- Topical gels and creams: You’ll apply these daily, and the testosterone will absorb slowly and evenly into the bloodstream. This method avoids the peaks and troughs men often experience with injections.
- Pellets: Your doctor will surgically implant these under your skin where they will release testosterone over several months. It’s a low-maintenance option, but it does require a minor in-office procedure.
Whichever method you opt for, your doctor will use regular blood tests to continuously monitor your treatment and results.
Working with a TRT Specialist
It’s important to choose the right TRT specialist for successful therapy. A qualified hormone specialist or endocrinologist will have a deep understanding of hormone replacement therapy and tailor your treatment to meet your specific needs. Your specialist will guide you through the treatment process, help you manage side effects, and adjust your dosage as necessary.
A skilled TRT specialist will also take into account any pre-existing conditions, such as cardiovascular issues or prostate health concerns, to ensure they don’t impact your TRT and vice versa.
Importance of Regular Blood Work
Routine blood work is the backbone of effective TRT management. Blood tests allow your doctor to monitor your testosterone and other hormone levels, such as estradiol (E2), dihydrotestosterone (DHT), prostate-specific antigen (PSA), and prolactin. They need to keep these hormones in balance to prevent common side effects and complications.
Blood work typically includes:
- Total testosterone levels: To ensure your testosterone is within the normal range
- Estradiol (E2) levels: To monitor estrogen levels, which can rise if your body converts testosterone into estrogen
- Hemoglobin and hematocrit: To ensure that TRT doesn’t cause an overproduction of red blood cells, which can increase the risk of blood clots
- Liver and kidney function: To ensure TRT does not cause any organ stress
Adjusting Treatment Based on Response
Your doctor will assess your body’s response to TRT over time through blood work and your subjective experience of symptom relief. If you experience too many side effects or don’t see enough symptom improvement, your specialist may adjust your:
- Dosage: They may increase or decrease your dose to find the sweet spot.
- Frequency: More frequent injections or a different application may help you maintain more stable hormone levels.
- Supplemental Medications: Doctors sometimes prescribe medications like aromatase inhibitors (to manage high estrogen) or hCG (to preserve fertility).
Adjustments are a normal part of the TRT journey, so be open and honest with your doctor about your status, changes, and any side effects.
8. Monitoring and Managing Side Effects
TRT can offer numerous benefits, but it’s important to monitor and manage potential side effects. Not all men will experience side effects, but knowing how to prevent or mitigate them ensures long-term success with therapy.
Common Side Effects and How to Manage Them
Elevated Estradiol (E2), DHT, and Prolactin
Testosterone doesn’t act in isolation. When testosterone enters the body, some converts into estradiol (E2) or dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which may lead to imbalances. High estradiol levels can cause water retention, mood swings, and gynecomastia (breast tissue enlargement), and high DHT levels often lead to acne and hair loss.
Prolactin levels may also rise, especially when testosterone is too high, and potentially affect mood and sexual function. To manage these side effects, your doctor may prescribe:
- Aromatase inhibitors (such as anastrozole) prevent testosterone from converting into estrogen and keep estradiol levels under control.
- DHT blockers (such as finasteride) can prevent DHT from affecting hair follicles and minimize hair loss.
Your doctor will use regular blood work to monitor and balance these hormone levels.
Strategies to Prevent Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia, or the enlargement of male breast tissue, can happen when estradiol levels rise too high as excess testosterone converts into estrogen. To combat this side effect, your doctor may:
- Lower the TRT dosage if estradiol levels are too high
- Use aromatase inhibitors to block the conversion of testosterone to estrogen
- Conduct regular blood tests to catch any rise in estradiol early.
In severe cases, patients may require surgical treatment, but this is generally a last resort.
Managing Cholesterol and Blood Pressure
TRT may cause an increase in LDL (bad cholesterol) and a decrease in HDL (good cholesterol). High cholesterol levels, combined with increased red blood cell production from TRT, can raise the risk of cardiovascular issues. To manage this:
- Follow a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Incorporate regular exercise—both strength training and cardiovascular workouts.
- Take prescribed medications if necessary to control cholesterol and blood pressure levels.
Your doctor will monitor these markers during regular blood tests to ensure your treatment doesn’t compromise your cardiovascular health.
Preventing Testicular Atrophy and Preserving Fertility
One of the potential side effects of long-term TRT is testicular atrophy (shrinkage of the testicles) and decreased sperm production. This happens because TRT can suppress the body’s natural production of testosterone in the testicles.
Your doctor will monitor your fertility markers and testosterone levels to catch and address any testicular atrophy issues early.
They may prescribe hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) alongside TRT to preserve fertility and prevent testicular shrinkage. hCG stimulates the testicles to produce testosterone and sperm, which helps maintain their size and function.
Work with a qualified specialist to ensure your Testosterone Replacement Therapy is safe, effective, and fits your unique needs. They will closely monitor your hormone levels, help you manage any potential side effects, and adjust the TRT protocol when necessary to minimize risks and allow you to enjoy the full benefits of TRT.
9. Best Practices to Optimize Men’s Health While on TRT
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) can significantly improve men’s health, but lifestyle changes can support and enhance the treatment. To maximize the benefits of TRT and ensure long-term well-being, men should incorporate exercise, proper nutrition, and stress management into their daily routines. These factors amplify the effects of TRT and contribute to overall physical and mental health.
Importance of Exercise and Strength Training
Exercise—especially strength training—helps you get more out of TRT. Testosterone plays a key role in muscle growth and recovery, and regular workouts maximize these effects. Strength training stimulates muscle protein synthesis for enhanced muscle growth and fat loss.
Key benefits of regular strength training include:
- Increased muscle mass: Combine TRT with resistance exercises like weightlifting to build and maintain muscles that can otherwise diminish with age.
- Improved fat loss: Strength training boosts metabolism and promotes fat loss, which complements testosterone’s effect on body composition.
- Bone health: Weight-bearing exercises increase bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis, which is especially important as men age.
Together, strength training and cardiovascular exercise boost heart health, support fat loss, and improve overall fitness.
Nutritional Guidelines to Maximize TRT Results
Eat a well-balanced diet to achieve optimal results from TRT. The right nutrients support hormone production, energy levels, and overall health to help TRT work more effectively.
Macronutrients, Vitamins, and Supplements
To complement TRT, focus on the following key nutrients:
- Protein: Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth. Aim to include plenty of lean protein sources, such as chicken, fish, eggs, and plant-based options like beans and lentils, in your diet.
- Healthy fats: Testosterone production relies on dietary fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids. Include sources like fatty fish, avocados, olive oil, and nuts in your meals.
- Carbohydrates: Carbs provide energy for workouts and muscle recovery. Choose complex carbs like whole grains, sweet potatoes, and vegetables for sustained energy.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Zinc, magnesium, and vitamin D are important for balanced testosterone levels. Eat foods like nuts, seeds, and spinach for healthy doses of zinc and magnesium, and spend adequate time in the sun for vitamin D synthesis or take a supplement.
Foods to Avoid While on TRT
Certain foods and substances can negatively impact testosterone levels or overall health. During TRT, limit your intake of:
- Excessively processed foods: Foods high in refined sugars and trans fats can lead to weight gain and hormone imbalances.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can suppress testosterone production and impair muscle recovery.
- Soy: Some studies suggest that large amounts of soy products may negatively affect testosterone, though the evidence is inconclusive.
Maintain a diet rich in whole foods and essential nutrients to support the hormonal balance and physical improvements of TRT.
Sleep, Stress Management, and Overall Wellness
While exercise and nutrition are vital, sleep and stress management are equally important to optimize your health while on TRT.
- Sleep: Testosterone production primarily occurs during deep sleep. Get 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to maintain healthy hormone levels and promote recovery from workouts. Sleep deprivation can negate some of the benefits of TRT and lead to suboptimal results.
- Stress management: Chronic stress raises cortisol levels, interfering with testosterone production and overall hormone balance. Meditation, yoga, and mindfulness can help reduce stress and support mental well-being.
- Overall wellness: Maintain a healthy balance between physical activity, mental health, and social connections to improve your overall wellness and amplify the benefits of TRT.
TRT is one part of a holistic approach to health, alongside exercise, nutrition, sleep, and stress management. With a whole-body approach, men can achieve their best physical and mental outcomes.
Conclusion
Weigh the Benefits and Risks of TRT
Testosterone Replacement Therapy can be transformative for men with low testosterone. It offers a range of benefits that include improved muscle strength, increased energy, better mood regulation, and enhanced sexual health.
However, before you start TRT, weigh these benefits against the potential risks, such as hormonal imbalances, cardiovascular concerns, and prostate health issues. Work with a qualified healthcare provider to monitor and manage these risks and ensure that TRT is a safe and effective option for you.
Take an Informed Approach to Testosterone Optimization
TRT is not a one-size-fits-all treatment. Different factors influence treatment approaches, potential side effects, and outcomes. For safe and effective treatment:
- Consult with a specialist who can accurately diagnose testosterone deficiency and recommend the best course of action.
- Monitor hormone levels regularly to ensure that your testosterone levels stay within the optimal range and minimize any side effects.
- Implement lifestyle changes, including exercise, nutrition, and stress management, to maximize the benefits of TRT and support overall health.
When you understand the potential risks, work with a qualified TRT specialist, and adopt a balanced approach to health, you can achieve lasting improvements through testosterone therapy.
The Long-Term Benefits of TRT for Men’s Health and Quality of Life
For men with testosterone deficiency, TRT can offer long-term benefits that greatly improve quality of life. From increased physical strength and better body composition to enhanced mood, mental clarity, and sexual performance, testosterone therapy can help men feel younger, stronger, and more vibrant. Combined with a healthy lifestyle, these benefits lead to sustained improvements in overall well-being and longevity.
Ultimately, TRT can be a powerful tool to restore and maintain men’s health as they age and promote a higher quality of life for years to come.
Not sure if you need a testosterone test?
Take our 2-minute quiz to see if you have the common symptoms of low testosterone and find out your hormonal age.
Testosterone replacement FAQs
What is Testosterone Optimization Therapy (TOT)?
TOT or Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) supplements testosterone to bring blood testosterone levels to the optimal high-normal range. It is a lifelong therapy designed to address age-related declines in testosterone production and testosterone deficiencies caused by lifestyle factors and environmental toxins. TOT aims to improve overall well-being, enhance physical and cognitive function, and mitigate the negative effects of aging.
Why are testosterone levels declining in men?
Testosterone levels in men have declined at an alarming rate over the past few decades. Several factors contribute to this decline, including:
- Aging: Natural testosterone production gradually decreases with age.
- Modern lifestyle: Poor diet, lack of exercise, stress, and inadequate sleep can negatively impact testosterone production.
- Environmental toxins: Exposure to xenoestrogens, chemicals that mimic estrogen in the body, can disrupt hormonal balance and lower testosterone.
- Obesity: Excess body fat, particularly visceral fat, can convert testosterone to estrogen and further contribute to the decline.
What are the benefits of TOT?
Optimizing testosterone levels through TOT can provide a wide range of benefits, including:
- Increased muscle mass and strength: Testosterone supports muscle protein synthesis, enhanced muscle growth, and strength.
- Reduced body fat: TOT can increase metabolism and promote fat loss for a leaner physique.
- Improved energy levels and mood: Testosterone helps regulate energy levels and mood, so TOT can combat fatigue and symptoms of depression.
- Enhanced libido and sexual function: Testosterone is essential for libido and erectile function. TOT can improve sexual desire and performance.
- Improved cognitive function: Studies show a link between optimal testosterone levels and improved memory, focus, and cognitive abilities.
- Increased bone density: Testosterone contributes to bone health, and TOT can help prevent osteoporosis and maintain strong bones.
What are the potential side effects of TOT?
TOT is generally safe when supervised by a qualified physician, but side effects can occur, including:
- Acne and oily skin: Increased testosterone can stimulate sebum production and cause acne breakouts.
- Hair loss: TOT may accelerate hair loss in men genetically predisposed to male pattern baldness.
- Prostate enlargement: Testosterone can stimulate prostate growth and potentially lead to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
- Erythrocytosis (increased red blood cell count): TOT can increase red blood cell production, which may thicken the blood and increase the risk of cardiovascular events.
- Mood swings and irritability: Some men may experience mood swings or increased irritability with TOT.
- Testicular atrophy: Exogenous testosterone can suppress natural testosterone production and cause testicular shrinkage.
How is TOT administered?
There are various TOT treatment methods, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
- Intramuscular injections: This is the most common method and requires testosterone injections into the muscle, typically every 1-2 weeks.
- Transdermal patches and gels: Testosterone is absorbed through the skin through patches or gels applied daily or weekly.
- Subcutaneous injections: This method involves testosterone injections under the skin, typically every few days.
- Pellets: Testosterone pellets are implanted under the skin, where they release testosterone slowly over several months.
- Buccal preparations: Testosterone tablets or troches dissolve between the gums and cheek for fast absorption into the bloodstream.
What is the difference between TOT and anabolic steroid use?
TOT and anabolic steroid use both involve testosterone injections, but there are key differences:
- Dosage: TOT uses therapeutic doses to replace or optimize natural testosterone levels, while anabolic steroid use involves supraphysiological doses to enhance muscle growth and performance beyond what’s naturally achievable.
- Goal: TOT aims to restore hormonal balance and improve overall health, while anabolic steroid use primarily focuses on maximizing muscle mass and strength.
- Medical supervision: TOT is prescribed and monitored by a physician to ensure safety and appropriate dosage, while anabolic steroid use is often done without medical supervision and poses significant health risks.
How do I find a qualified TOT doctor?
A qualified TOT specialist is crucial for safe and effective treatment. Here’s what to look for:
- Specialized training: Look for a physician who specializes in hormone therapy, such as an endocrinologist or urologist with experience in men’s health.
- Comprehensive evaluation: A qualified TOT doctor will conduct a thorough medical history, physical exam, and lab tests to assess your testosterone levels and overall health.
- Personalized treatment plan: They will develop a personalized treatment plan based on your needs and goals and weigh the potential risks against the benefits.
- Ongoing monitoring: Your TOT doctor should monitor your hormone levels, blood work, and overall health regularly to ensure safety and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
- Open communication: Choose a doctor who listens to your concerns, answers your questions, and involves you in the decision-making process.
Can I still have children while on TOT?
TOT can temporarily suppress sperm production and potentially affect fertility. To preserve or restore fertility while on TOT, your doctor may suggest:
- hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin): hCG injections can stimulate testosterone production in the testicles and maintain sperm production.
- Clomid (clomiphene citrate): Clomid can stimulate the pituitary gland to release hormones that promote sperm production.
- hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin): hMG injections contain hormones that stimulate sperm production.
- Sperm banking: As a backup option, you may choose to freeze your sperm before you start TOT.
Discuss your fertility goals with your TOT doctor to determine the best approach for you.